Static Variables and Static Class Members
Static Object : Summary About Static Variable and Static Class
1. Persistence : it remains in memory until the end of the program.
2. File Scope : it can be seen only withing a file where it's defined.
3. Visibility : if it is defined within a function/block, it's scope is
limited to the function/block. It cannot be accessed outside of the
function/block.
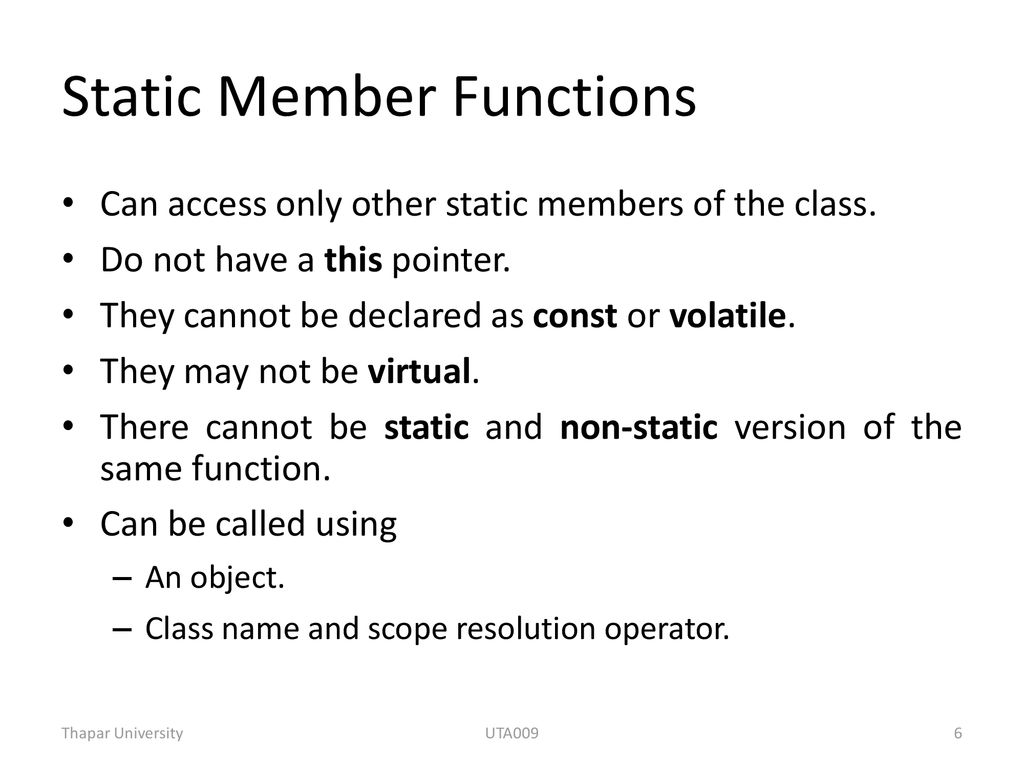
4. Class : static members exist as members of the class rather than as an instance in each object of the class. So, this
keyword is not available in a static member function. Such functions
may access only static data members. There is only a single instance of
each static data member for the entire class:
A static data member : class variable
A non-static data member : instance variable
5. Static Member Function : it can only access static member data, or other static member functions
while non-static member functions can access all data members of the class: static and non-static.
Example
#include <QApplication>
#include<QDebug>
class MyClass
{
public:
static void staticFunction(){
qDebug()<<"This Is The Static Memeber Function of My Class";
}
static int x;
private:
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
MyClass::staticFunction();
return 0;
}


